The risk of heat stress is increased in hot, humid climates like the UAE. The average temperature in the UAE can reach up to 49 degrees Celsius (120 degrees Fahrenheit) in the summer, and the humidity can be as high as 79%. This combination of heat and humidity can make it difficult for the body to cool down, which can lead to heat stress.
Heat stress is a serious health hazard that can affect anyone who works or exercises in hot weather. It can lead to heat cramps, heat exhaustion, and even heat stroke, which can be fatal.
To give you some perspective on heat injury, here are some statistics on the effects of extreme temperatures according to the World Health Organization:
- 166,000 fatalities from 1998-2017
- 250,000 predicted additional deaths each year from 2030
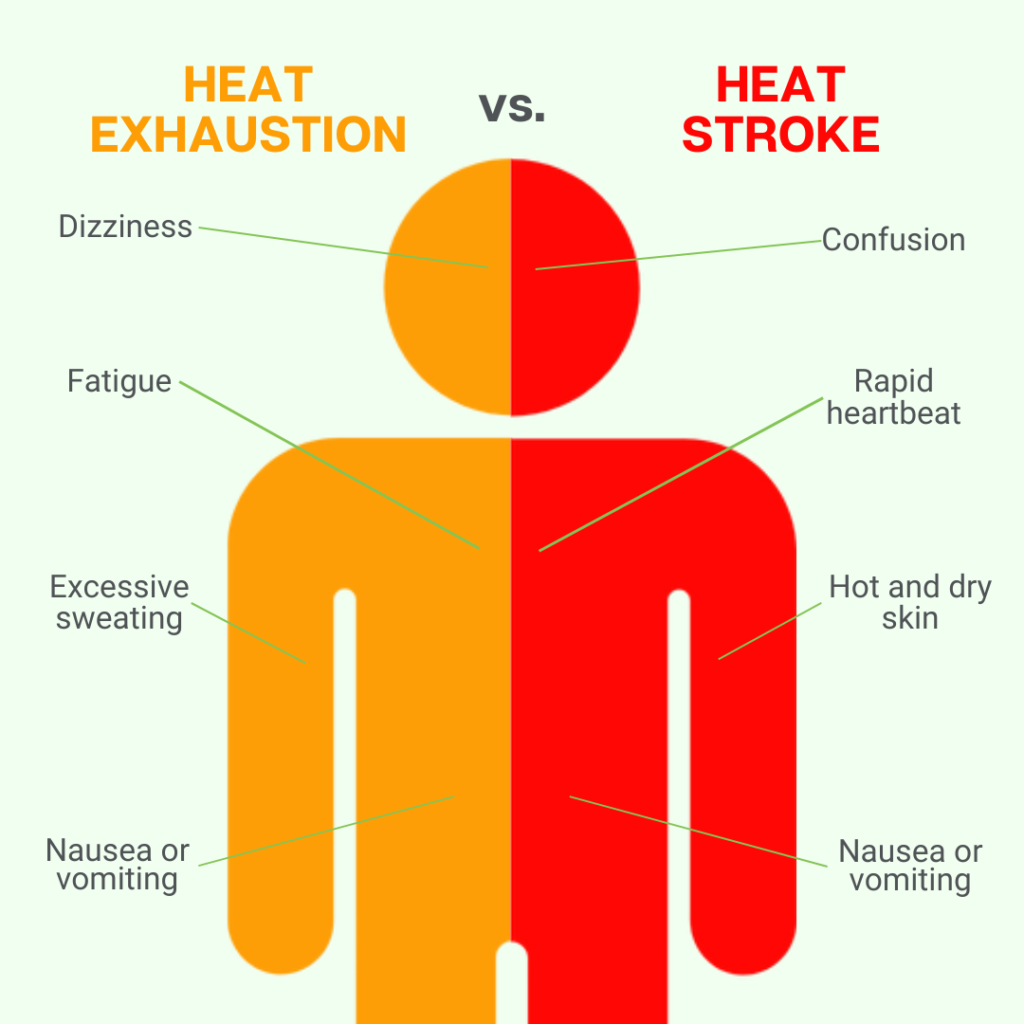
Some common early signs of heat stress include fatigue, dizziness, excessive sweating, and nausea. The more serious symptoms that you need to watch out for are confusion, rapid heartbeat, hot and dry skin, and fainting. Severe symptoms of heat stress could lead to a heat stroke. If you experience any of these symptoms, you should seek medical attention immediately.
But what makes us feel warmer
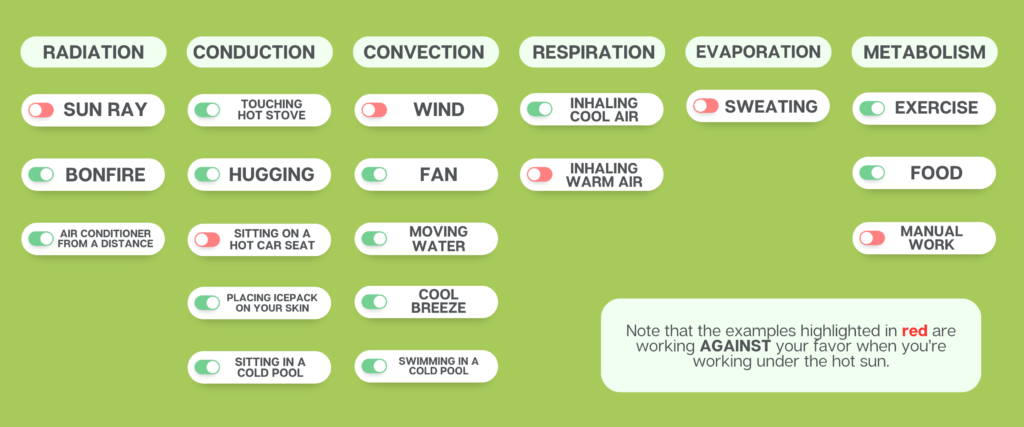
Before diving into the prevention methods of heat stress, it’s important to identify the sources of heat when we exercise or work outside (Table 1).
There are five main sources of heat that you need to consider especially when you are working outside namely: radiation, conduction, convection, respiration, and evaporation. Metabolism can be considered an internal source of heat, which releases heat from chemical reactions happening inside the body when we break down food and exercise.
How can you prevent heat stress?
In principle, preventing and reducing heat stress is about managing the five main heat exchange mechanisms depicted in Table 1. To achieve this, there are a number of methods that can be applied to prevent heat stress, including:
- Stay hydrated. Drink plenty of fluids, especially water, before, during, and after working or exercising in hot weather. Aim to drink 16 ounces of fluids for every hour of activity. Other fluids that are hydrating include fruit juices without added sugar, milk, sports drinks, green tea, watermelon, and other fruits and vegetables with high water content.
- Wear loose-fitting, light-colored clothing. This will help your body to cool down by evaporation. Avoid wearing dark or tight-fitting clothing, as this can trap heat. Some good fabric choices for hot weather include cotton, linen, rayon, and bamboo.
- Take breaks in shaded areas. If you are working or exercising outside in the hot weather, it is important to take regular breaks in a shaded area. This will give your body a chance to cool down and prevent heat stress.
- Avoid strenuous activity during the hottest part of the day. If possible, try to schedule strenuous activities for the cooler parts of the day, such as early morning or evening.
- Acclimatize yourself to the heat. If you are not used to working or exercising in hot weather, it is important to gradually acclimatize yourself to the heat. This can be done by gradually increasing the amount of time you spend in hot weather.
- Wear sun protection. Wearing a hat and sunglasses can help to protect your head, face, and eyes from the sun’s harmful rays. Applying sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher can help to protect your skin from sunburn.
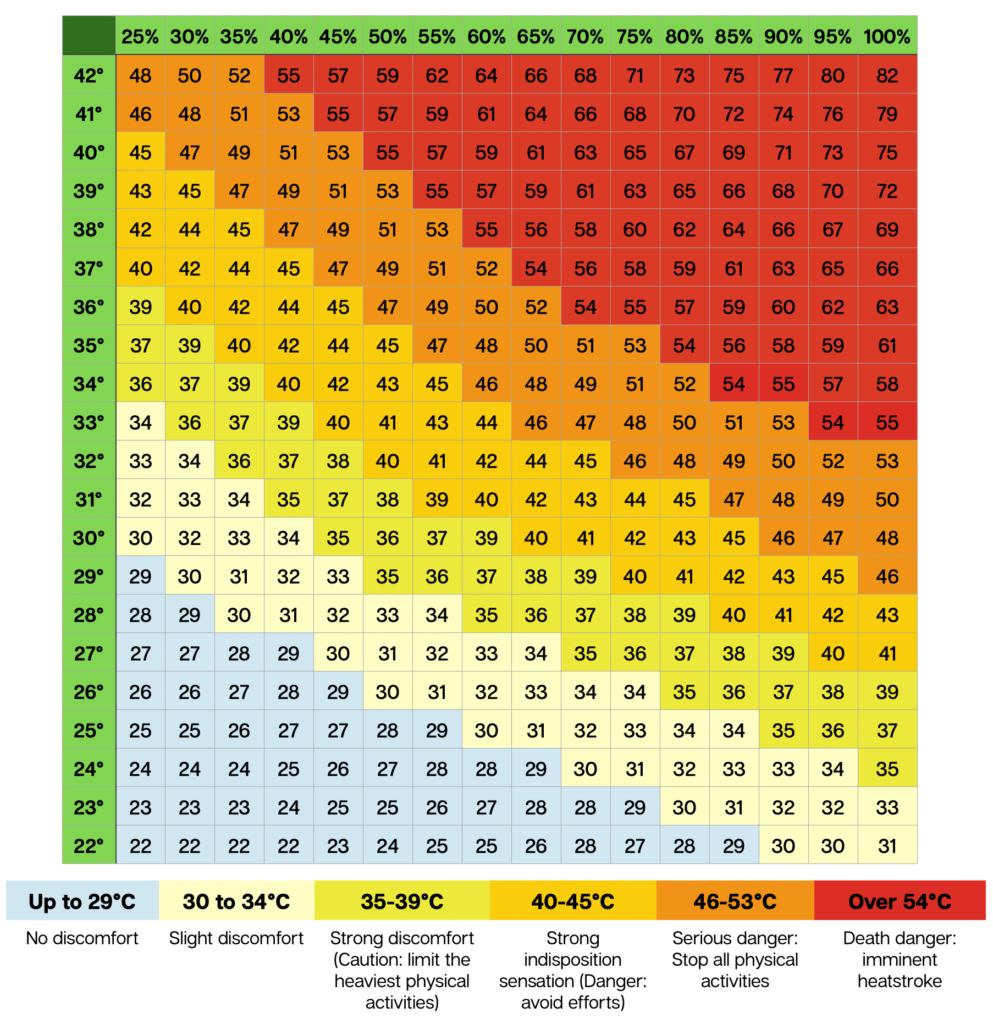
- Check the heat index before you go outside. The heat index is a measure of how hot it feels when the humidity is factored in. If the heat index is high, it is important to take extra precautions to avoid heat stress. A heat index of 40 degrees Celsius or higher is considered dangerous.
Office Wellness
Heat stress can also have a negative impact on office wellness. The hot weather in the UAE makes it important for organizations to take steps to prevent heat stress among their employees. Organizations should provide employees with access to cool water, shade, and rest breaks. They should also train employees on the signs and symptoms of heat stress and how to treat it. Additionally, organizations can provide accessible parking locations that are close to the office with shaded walking trails/sidewalks to help employees stay cool and hydrated on their way to and from work.
Applying the following recommendations and staying up to date with leading practices and guidelines creates a culture that encourages employees to take care of their health and to report any concerns about heat stress, thus preventing and reducing the chances of developing heat illnesses such as heat exhaustion and heat strokes.
Discover more from WellFit
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.




I was pretty pleased to discover this website. I wanted to thank you for your time for this particularly fantastic read!! I definitely savored every part of it and i also have you saved as a favorite to see new stuff on your web site.
דירות דיסקרטיות בבת ים
I’ve read a few excellent articles here that are definitely worth saving for future reference. I’m curious about the amount of work you put into making such a wonderful and educational website.